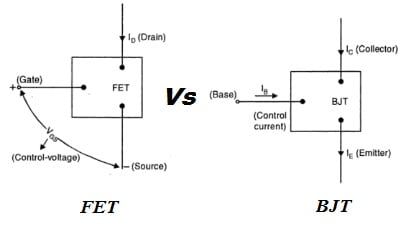
The basic differences between BJT and FET is that the former is a current-controlled device and later is a voltage-controlled device. In the case of BJT the prefix “Bi” comes out from the fact that a BJT have both types of charge carriers i.e., electrons and holes, but in the of a FET, either electrons or holes constitute the drain current, so named as unipolar transistor. Depending upon the type of charge carriers, FETs have been classified as n-channel or p-channel FET or in other words we can say that the operation of FET depends upon the flow of majority carries only. There are a large number of advantages of FET over BJT. But, the main disadvantage of FET is its relatively small gain bandwidth-product in comparison with that which can be obtained with a conventional bipolar transistor.

Difference Between FET and BJT
Following are the few differences between BJT and FET which must be known to the students before discussing FET’s operation in detail.
| S.No. | FET | BJT |
| 1 | FET is an unipolar semiconductor device because its operation depends upon the flow of majority carriers i.e., either holes or electrons as the case may be. | BJT is a bipolar semiconductor device because the current constituting elements are both majority carriers as well as minority carriers in this case. |
| 2 | The input impedance of FET is much more larger (ranging in Mega ohms) than BJT. The reason behind this is that the input terminal i.e., gate to source of FET is reverse biased and reverse bias offers ideally infinite resistance. | The input impedance of BJT is very leas in comparison to FET. |
| 3 | FET is a voltage controlled device. | BJT is a current controlled device. |
| 4 | FET is less noisy. Because there are no junctions. | Much noisy than FET. |
| 5 | Higher frequency response. | Frequency variation affects the performance. |
| 6 | Good thermal stability because of absence of minority carriers. | Temperature dependent, thermal runaway may cause. |
| 7 | Costlier than BJT. | Relatively cheaper. |
| 8 | Small sized. | Comparatively bigger. |
| 9 | In FET, relationship between input and output quantities is nonlinear due to square term in shockley’sequations I_{D}=I_{DSS}\left ( 1-\frac{V_{GS}}{V_{P}} \right )^{2} | The BJT is an almost linear device or we can say that BJT works linearly in active region as an amplifier. |
| 10 | No offset voltage; so it works better as a switch or chopper. | There is always an offset voltage before switching. |
| 11 | Small gain bandwith product. | Greater than FET. |
Comparison Between Field-effect Transistor and Bipolar Junction Transistor
- Field Effect Transistor is a unipolar device i.e., the current in the device is carried either by electrons or holes whereas Bipolar Junction Transistor is a bipolar device, i.e., the current in the device is carried by both electrons and holes.
- FET is a voltage-controlled device, i.e., the voltage at the gate (or drain) terminal controls the amount of current flowing through the device whereas BJT is a current-controlled device, i.e., the base current controls the amount of collector current.
- The input resistance of FET is very high and is of the order of several megaohms whereas the input resistance of BJT is very low and is of the order of few kilo-ohms.
- FET has a negative temperature coefficient at high current levels. It means that the current decreases as the temperature increases. This characteristic prevents the FET from thermal breakdown whereas BJT has a positive temperature coefficient at high current levels. It means that the collector current increases with the increase in temperature. This characteristic leads the BJT to thermal breakdown.
- Field Effect Transistor does not suffer from minority-carrier storage effects and therefore, has higher switching speeds and cut-off frequencies whereas Bipolar Junction Transistor suffers from minority carrier storage effects and therefore, has lower switching speed and cut-off frequencies than that of FET’s.
- FET is less noisy than a BJT or vacuum tube and is thus more suitable as an input amplifier for low-level signals. It is used extensively in high fidelity frequency-modulated receivers whereas BJT is comparatively more noisy than a field-effect transistor.
- FET is much simpler to fabricate as an integrated circuit (IC) and occupies less space on the IC chip whereas BJT is comparatively difficult to fabricate as an integrated circuit (IC) and occupies more space on IC chip than that of FET.
Related Posts:
Difference Between Dual Trace and Dual Beam CRO